Many-to-Many Relations
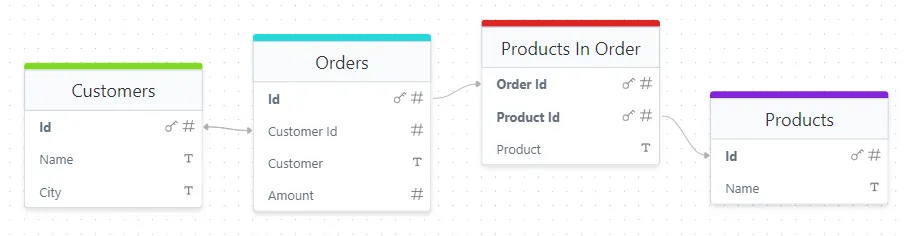
In some applications, an entity might need to have a relationship with multiple entities from another table, and vice versa. In our case, an Order can contain many Products, and the same Product can appear in many Orders. This is a classic many-to-many relationship.
To implement this relationship, we use an intermediate entity called ProductInOrder, which serves as a bridge between Order and Product. This intermediate entity stores the association between an order and a product, along with additional details that pertain to the relationship, such as quantity or price, if needed.
Defining the Many-to-Many Relation
Let’s define the ProductInOrder entity, which establishes the many-to-many relation between Order and Product.
import { Entity, Fields, Relations } from 'remult'import { Product } from './Product'
@Entity<ProductInOrder>('ProductsInOrder', { allowApiCrud: true,
id: ['orderId', 'productId'], // Composite Primary Key})export class ProductInOrder { @Fields.integer() orderId = 0 @Fields.integer() productId = 0 @Relations.toOne<ProductInOrder, Product>(() => Product, 'productId') product?: Product}Key Points
-
Composite Primary Key:
We define the composite primary key using bothorderIdandproductId(id: ['orderId', 'productId']). This ensures that the combination of these two fields uniquely identifies each record inProductInOrder. Using a composite key improves performance when querying or joining tables because it provides a direct and efficient way to locate specific rows. -
Relation to
Product:
The@Relations.toOne()decorator establishes a relationship betweenProductInOrderand theProductentity. This allows us to easily fetch the relatedProductinformation (such as the name or price) when queryingProductInOrder.
Defining the Order Entity
In the Order entity, we use a toMany relation to link each order to its products through the ProductInOrder entity. This allows us to keep track of all the products in a particular order.
4 collapsed lines
import { Entity, Fields, Relations } from 'remult'import { Customer } from './Customer'import { ProductInOrder } from './ProductInOrder'
@Entity('orders')export class Order { @Fields.integer()6 collapsed lines
id = 0 @Fields.integer() customerId = 0 @Relations.toOne<Order, Customer>(() => Customer, 'customerId') customer!: Customer @Fields.number() amount = 0 @Relations.toMany<Order, ProductInOrder>(() => ProductInOrder, 'orderId') products?: ProductInOrder[]}Querying the Data
When you want to fetch the data, including the related products, you can use the include option to fetch not only the ProductInOrder records but also the corresponding Product details.
repo(Customer).find({ include: { orders: { include: { products: { include: { product: true, // Fetch product details such as name, price, etc. }, }, }, }, },})Why Not Use a Built-in Many-to-Many Feature?
A natural question arises: why not create a built-in many-to-many relation directly between Order and Product without an intermediate table?
The reason is that most many-to-many relationships in real-world applications are not that simple. Typically, you will need to store additional information about the relationship itself, such as quantity, pricing, discounts, or status. By using an intermediate entity like ProductInOrder, you have the flexibility to store these additional attributes alongside the relationship. This approach is much more versatile and better suited to real-world use cases than a basic many-to-many relation, which can be too limited for most scenarios.
Summary
In this lesson, we’ve learned how to model many-to-many relationships using an intermediate table. By creating the ProductInOrder entity, we’ve enabled a flexible many-to-many relationship between Order and Product. This approach allows us to include additional fields, such as quantity, in the relationship while maintaining optimal performance through the use of composite keys.
- Installing dependencies
- Starting http server